Given problem
- The structure of Drools Language
- Declaration part
- Implementation part with statements
- MVEL dialect
- How to use variable in Drools
- How to resolve conflicts when there are multiple the same conditions
- Wrapping up
The structure of Drools Language
Belows are some parts in Drools Language that we need to know.
-
Declaration part
-
Implementation part with statements
Declaration part
The first thing when we want to define rules in .drl file is to declare package that this file is contained, and the following lines is places of classes that we use.
package <package_name>
import <class_in_package>
import <class_in_package>
For example:
package com.manhpd.rule1
import com.manhpd.domain.Customer;
import com.manhpd.domain.Employee;
Implementation part with statements
-
Declare rules’s name and attributes
rule "rule_name" <define_attributes> endIn the define_attributes option, we usually define a dialect. Dialect is used to define the syntax for our code logic such as conditions, …
The default dialect is Java. But we can use the additional MVEL expression language in drl file. MVEL supports the getter/setter methods.
Belows are some common attributes that Drools makes.
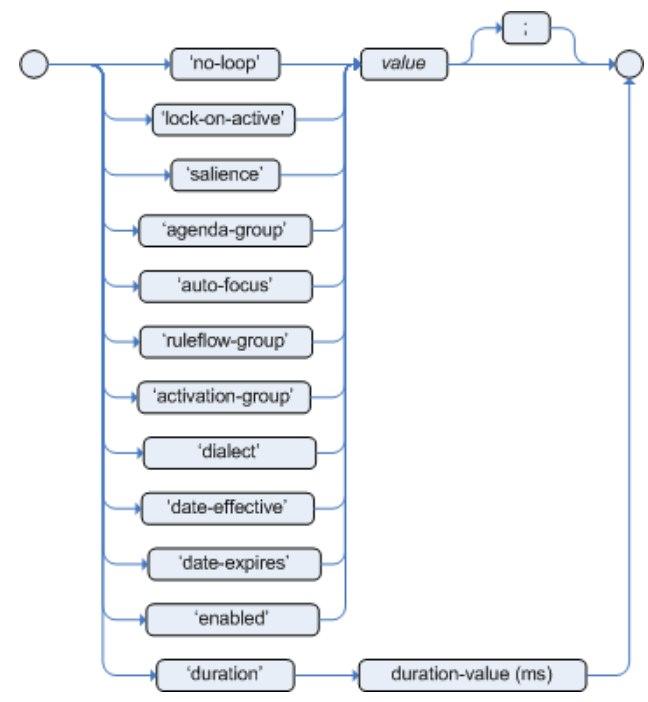
-
The structure of Rule
when <conditions> then <actions>If conditions are true, then our actions will be implemented. Sometimes, conditions can be called LHS - Left Hand Side, actions called as RHS - Right Hand Side.
-
For example
rule "rule_name" dialect "mvel" when <conditions> then <actions> end
MVEL dialect
-
Common operations
-
Equal
- ClassName(condition1, condition2, …)
- ClassName(condition1 && condition2 && …)
-
Use OR construct
Classname(condition1 || condition 2 || …)
-
Value correction
For example: “3456” = 3456
-
-
Expressions in MVEL and Java
-
Get the value of a field in an object
-
Java:
employee.getAge(); -
MVEL:
employee.age
-
-
Get the value of a field with checking null
-
Java
if (employee.getAddress() != null) { return employee.getAddress().getDistrict(); } return null; -
MVEL:
employee.?address.district
-
-
Compare strings
-
Java:
"John".equals(employee.getName()); -
MVEL:
employee.name == '50'
-
-
Check whether a list contains an item or not
- Java:
Arrays.asList("John Wick", "Jack").contains(employee.getName());
- Java:
-
Check null for an object
-
Java:
employee == null -
MVEL:
employee == niloremployee == null
-
-
Set value for a field of an object
-
Java:
employee.setName("Johnson") -
MVEL:
employee.name = "Johnson"oremployee.name = 'Johnson'
-
-
-
Collections in MVEL
-
Lists
- names = [“John Wick”, “Jack Reacher”]
- names[0]
-
Arrays
- {“John Wick”, “Jack Reacher”}
-
Strings are arrays:
- name = “John”;
- name[0]
-
Maps
- person = [“first_name” : “John”, “last_name” : “Wick”]
- person[“first_name”]
- person.first_name
-
How to use variable in Drools
Assuming that we have the model of Employee, it will be describe the below source code.
public class Employee {
private int age;
private int name;
private String address;
// get, set
}
// definition of drl file
global com.manhpd.statistics.NumEmployee numEmployee;
rule "Age validation of Employee"
dialect "mvel"
when
$employee: Employee(age > 18)
then
System.out.println("Information of employee that is enough age: " + $employee);
numEmployee.increment();
end
So, we should use $ symbol with a name to define a variable. And Drools can work with the native Java types.
If we want to define a global variable in a session, use the global keyword.
How to resolve conflicts when there are multiple the same conditions
Using salience keyword to set the priority for each rule. The default value of salience is 0, but it can be negative or positive.
If a rule has a higher priority, it will be implemented first.
For example:
rule "higher priority"
salience(5)
when
<conditions>
then
<actions>
end
Wrapping up
- Understanding about MVEL expression language to define rules in drl file.
Refer:
https://docs.drools.org/5.3.0.CR1/drools-expert-docs/html/ch05.html
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/drools/drools_rule_syntax.htm
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/drools/drools_rules_writing.htm
http://support.streamx.co/intro/basic-drools-rule-language-syntax-cont