Table of contents
Given problem
Before Docker was born, we usually use Virtual Machine software such as VMWare, Virtual Box, … But to use it, we need to install the Operating System that we want to simulate the webserver’s environment that we want to use.
Then, we have to install softwares that we really need in out project. Installing these softwares takes so much our time.
Supposed that we had the environment that we want, but our softwares that has multiple versions, different environment variables to configure. They can conflict together. It is the worst thing that we do not want to touch.
How do we overcome these problems?
Introduction to Docker
-
History of Docker
Accroding to the wikipedia.com, we have:
Docker Inc. was founded by Solomon Hykes and Sebastien Pahl during the Y Combinator Summer 2010 startup incubator group and lauched in 2011. Hykes started the Docker project in France as an internal project within dotCloud, a platform-as-a-service company. In 2017, Docker created the Moby project for open research and development.Below is an image that describes the development of containers.
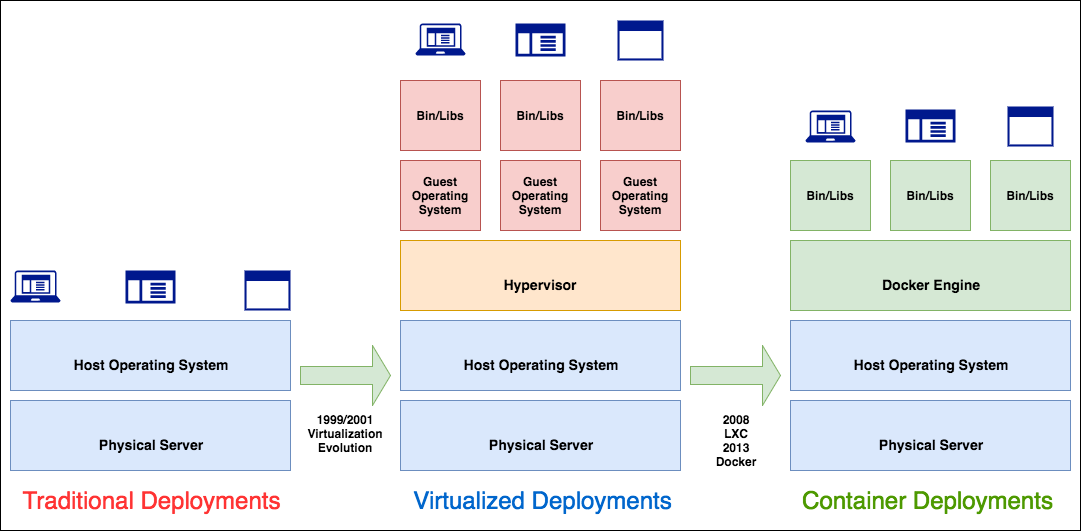
-
Some concepts in Docker
-
Docker is a software that helps us to build, deploy, and run our applications.
Docker will package our applications into containers.
For example, in our Java project, we need to use redis, mysql, mongodb, glassfish application server. Then, each application will be run in other containers. To be easily maintainable, we can create an image by using DockerFile.
To combine containers into a completely system, we need to use Docker Compose.
-
Docker Image basically contains executable application source code as well as the tools, libraries, and dependencies that our application code needs to run as a container.
Every Docker Image consists of one or more file system layers that generally have a direct one-to-one mapping to each individual build step used to create that image.
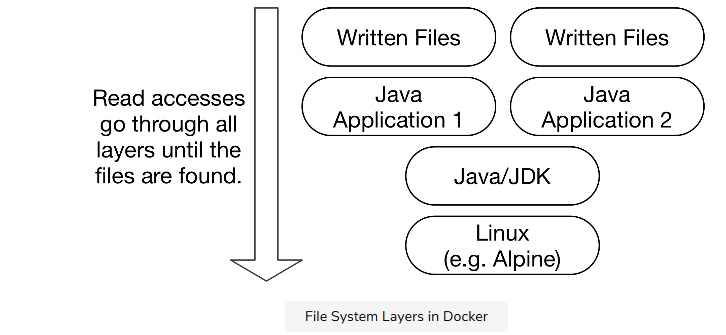
-
Docker Container is an instance of Docker Image.
This relationship is as same as the relationship between program and process.
A container runs inside the Docker Host isolated from the other containers and even the Host OS. It can not see the other containers, physical storage, … It contains everything it needs to run: OS, packages, runtimes, files, environment variables, standard IO.
-
DockerFile is a script file that guide Docker how to build an image.
To be aware more about DockerFile, we can read about an article How to build an image from DockerFile.
-
Registry is a place that contains multiple images.
-
-
The architecture of Docker
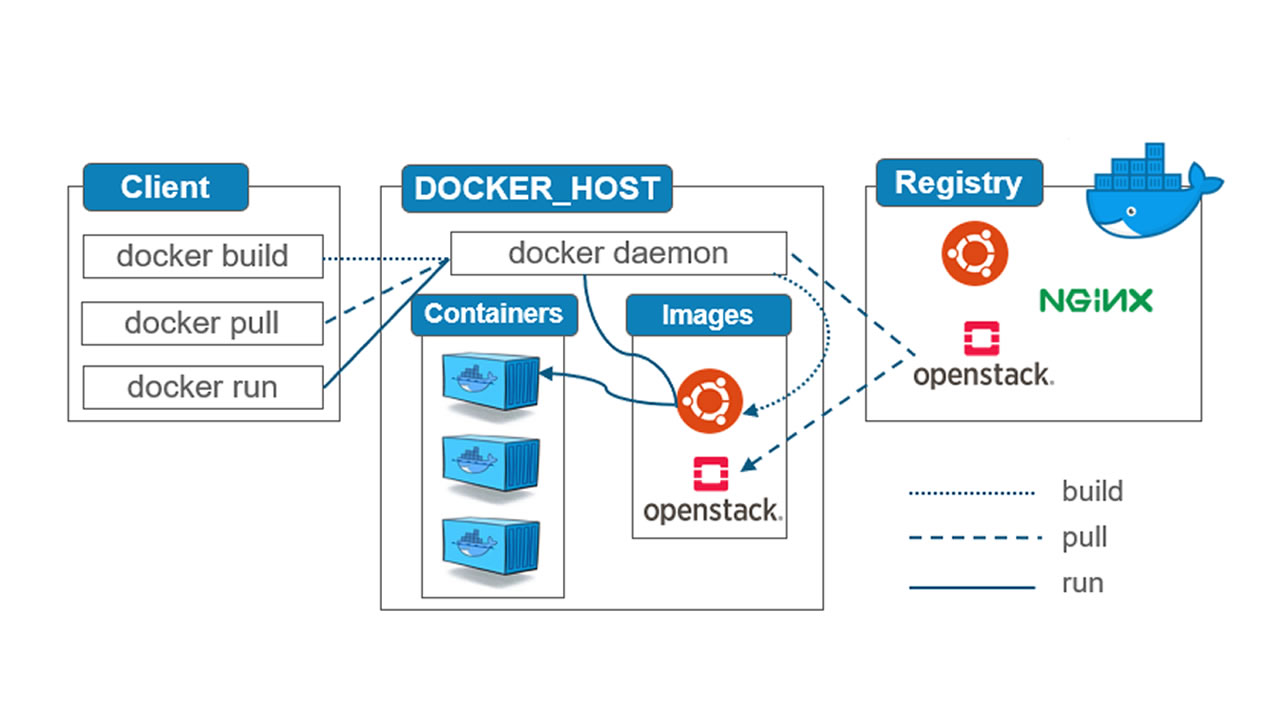
This article Docker Architecture Tutorial for Beginners will show the details of Docker’s architecture.
How to setup Docker
-
In Windows
-
Download Docker Desktop for Windows
Before setting up Docker on Windows, we need to install or upgrade WSL to WSL 2. We can check it on the following page: The guide to install WSL 2 on Windows 10
To install Docker for Windows, we need to download docker desktop from https://hub.docker.com/editions/community/docker-ce-desktop-windows/.
Click Get Stable button to download Docker.
-
Setup Docker desktop for Windows
After setting up Docker completely, we need to restart Windows OS.
-
Check Docker is setup completely by using a below command line.
docker --versionThen, we have:
-
-
In Ubuntu
To install Docker in Ubuntu, we can read the article How To Install and Use Docker on Ubuntu 18.04. It’s very detailed and easy to track steps.
Some commands in Docker CLI
-
Commands with images
-
List all local images that are downloaded from Docker Hub
# 1st way docker image ls # 2nd way docker images -
Pull an image from Docker Hub and run a container
docker run <image_name> # call help docker run --helpFor example, below is a command that pull ngix webserver from DockerHub and run it as a container.
docker run --detach --publish 80:80 --name webserver ngixThe meaning of options in an above command:
-
--detachor-dIn Docker, there are two mode:
- the background mode or a detach mode
- the default foreground mode
If we use –detach or -d option, it means that we want this container run in a detached mode.
-
--exposeUsing this flag is a way of documenting which ports are used, but does not actually map or open any ports. Exposing ports is optional.
-
--publishor-pBy default, when you create a container, it does not publish any of its ports to the outside world. To connect to the outside, we use
-poption.This option means that mapping a host port to a running container port.
For example:
docker run -d -p <host_port>:<container_port> --name webserver ngix -
--nameAssign a name for this container. If we do not use a name for a container, Docker will generate a random string name for a container.
-
-rmUsing this option will remove our container when it exits.
To know more about this run command, we can refer this Docker’s article https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/run/.
-
-
Pull an image from Docker Hub
docker pull <image_name> -
Remove an image
# Use image_id to specify which image to delete docker rmi <image_id> # Use the repository's name that combines with the tag docker rmi <repository_name>:<tag>For example:
# Use -f flat to forcely remove an image docker rmi -f fd484f19954f docker rmi test:latest -
Build an image from DockerFile
docker build --file <dockerfile_name> . -
Search an image from Docker Hub
docker search <image_name>For example:
docker search mysql -
Remove all images
docker rmi $(docker images -q) -
Push an image to the Docker hub
docker push <username/image_name>
-
-
Commands with containers
-
List all containers that are running in Docker engine
# 1st way docker ps # 2nd way docker container ls --all # call help docker container --help docker container ls --help -
Stop a container
docker container stop <container_name> -
List all containers with some specific states
# all the running and shutdowned containers docker ps -a # show all shutdowned containers with only numeric IDs docker -ps -a -q # show containers with disk usage docker ps --size # filter some containers with key=value pair docker ps --filter 'exited=0'-a flag means that we need to get all the containers with status = CREATED, RUNNING, EXITED.
-
Run a container
docker start <container_name> -
Restart a container
docker restart <container_name> -
Stop one or more containers
This command makes Docker wait for some minutes to a container shutdown.
# Stop a specific container docker stop <container_id> # Stop all running containers docker stop $(docker ps -a) -
Stop a container immediately
docker kill <container_id> -
Remove one or more containers
# Remove a stopped container docker rm <container_id> # Remove all shutdowned containers docker rm $(docker ps -aq) -
Access to the running container
docker exec -it <container_name> bash
-
-
Information of Docker
-
To check version of Docker Client/Server
# Only check version without the detailed information docker --version # verbose information about Docker Client/Server docker version -
Login to the Docker hub repository
docker login
-
-
Read log of a container
docker logs -f <container-name> -
Access to the docker container
Assuming that we want to create a MySQL database that attaches its internal /var/lib/mysql directory to a volume within the host directory mysql-data.
docker run --name mysql -v mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=passwd -d mysql:latestTo access the mysql’s environment, typing the below command:
docker exec -it <container-id/name> /bin/bash ls /var/lib/mysqlThe meaning of the above command:
-
docker exec [OPTIONS] CONTAINER COMMAND [ARG…] command runs a new command in a running container.
COMMAND will run in the default directory of the container. If the underlying image has a custom directory specified with the WORKDIR directive in its Dockerfile, this will be used instead.
Belows are some options of docker exec command.
Name Description –detach, -d Detach mode: run command in the background –env, -e set environment variables –interactive, -i keep STDIN open even if not attached –tty, -t Allocate a pseudo-TTY -
docker exec -it mysql /bin/bash command
We will execute an interactive bash shell on the container. This will create a new bash session in the mysql container.
To check where the mounted data from mysql container, we can go to the following /var/lib/docker/volumes/mysql-data/ directory. If we mount from the host directory such as -v ~/mysql-data:/var/lib/mysql, then the host directory ~/mysql-data will have the full path - /home/username/mysql-data.
-
Wrapping up
- Understanding about Docker and common commands that we usually use to communicate with it.
Refer:
https://medium.com/edumall/vi%E1%BA%BFt-dockerfile-hi%E1%BB%87u-qu%E1%BA%A3-77a6603b8f8
https://viblo.asia/p/docker-nhung-kien-thuc-co-ban-phan-1-bJzKmM1kK9N
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Docker_(software)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20274162/why-do-you-need-a-base-image-with-docker