Table of contents
- Given problem
- Node of a Tree
- Degree of a Node
- Edge, Path, and Distance
- Depth, Level, Height, and Width
- Wrapping up
Given problem
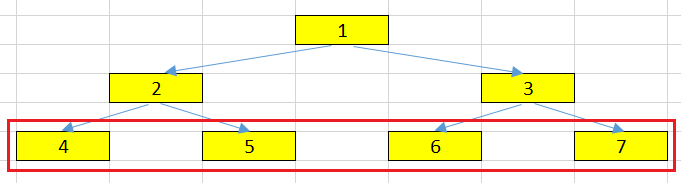
Given a tree that looks like an below image.
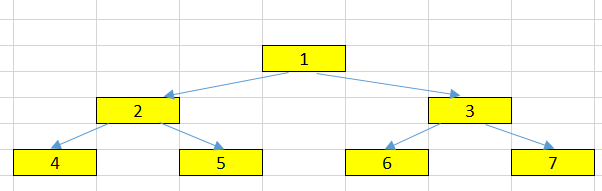
In this article, we will understand some common concepts such as:
- Node and some things around it.
- Degree
- Edge
- Path
- Distance
- Depth
- Level
- Height
- Width
Node of a Tree
A node is a structure which may contain a value or condition, or represent a separate data structure.
In an above image, we can have some nodes:
Normally, in binary tree, we can define a node like that.
class TreeNode {
int value;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
}
Belows are some concepts that are relevants to a Node.
-
Root node
The top node in a tree, the prime ancestor.
For example, our root node in an above tree is
1. -
Child node
A node directly connected to another node when moving away from the root, an immediate descendant.
For example,
2and3are the child nodes of theroot node-1. -
Parent node
The converse notion of a child, an immediate ancestor.
For example, 1 is the parent node of two child nodes: 2 and 3.
-
Sibling nodes
A group of nodes with the same parent.
For example, 2 and 3 are the sibling nodes. They have the same parent node - 1.
-
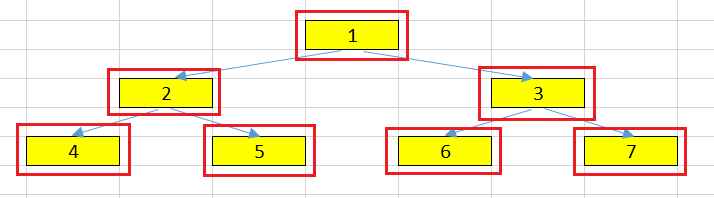
Descendant node
A node reachable by repeated proceeding from parent to child. Also known as subchild.
For example, 3, 7, and 6 are descendant nodes of 1.
-
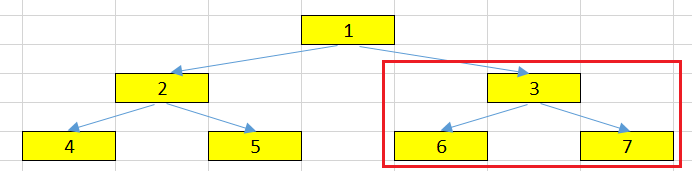
Ancestor node
A node u is an ancestor of a node v if v is contained in the subtree rooted at u; we may write equivalently that v is a descendant of u.
For example, 1 is an ancestor node for every node such as 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
-
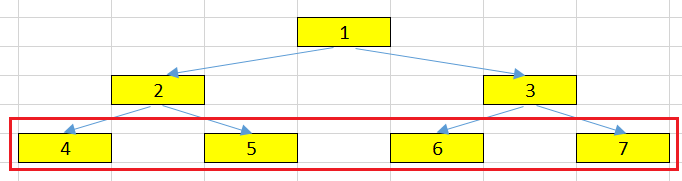
Leaf node
A node with no children.
For example, 4, 5, 6 and 7 are leaf nodes in our tree.
Degree of a Node
For a given node, it’s the number of children. A leaf is necessarily degree zero.
The degree of a tree is the maximum degree of a node.
For example:
- the degree of node 1 is 2 because it has two nodes: 2 and 3.
- the degree of an above tree is 2.
Edge, Path, and Distance
-
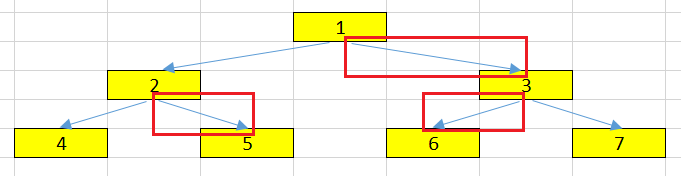
Edge
Edge is the connection between one node and another.
-
Path
Path is a sequence of nodes and edges connecting a node with a descendant.
Path includes all nodes and all edges along the path, not just edges.
For example, the path between two nodes 4 and 5 is: 4 –> 2 –> 5.
-
Distance
The number of edges along the shortest path between two nodes.
For example, the distance between 4 and 5 is 2.

Depth, Level, Height, and Width
-
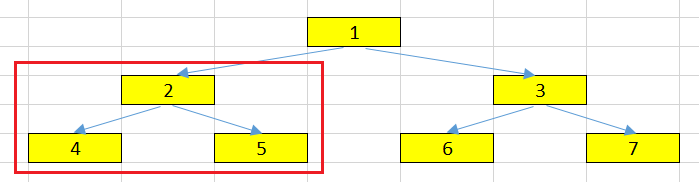
Depth
The distance between a node and the root.
The depth of the root node is 0.
For example, the depth of 5 node is 2.
-
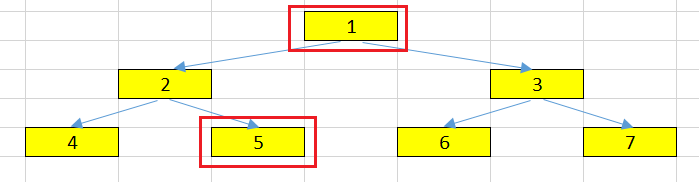
Level
The level of a node is defined by 1 + the number of edges between the node and the root.
Below is the relationship between Level and Depth concepts.
Level = Depth + 1The level of root node is 1.
For example, the level of 6 node in an above tree is 3.
Below is the source code that calculates the maximum level of binary tree.
We use top-down recursive version for this problem because:
- the starting point is the root node.
- we know that the level of root node is 1.
public class MaxLevelTree { private static int maxHeight = Integer.MIN_VALUE; private static void getMaxLevelTopDown(TreeNode root, int level) { if (root == null) { return; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, level); } getMaxLevelTopDown(root.left, level + 1); getMaxLevelTopDown(root.right, level + 1); } } -
Height
The height of a node is the number of edges on the longest downward path between that node and a leaf.
For example:
- the height of root node is 2.
- the height of 2 node is 1.
Below is the source code to calculate the height of binary tree. We will use bottom-up recursive version because:
- if the node is null, then its height is -1.
- the leaf node’s height is 0.
- It means that we have sufficient information about the height of the children nodes.
public static int getHeightTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return -1; } int leftHeight = getMaxLevelBottomUp(root.left); int rightHeight = getMaxLevelBottomUp(root.right); return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; } -
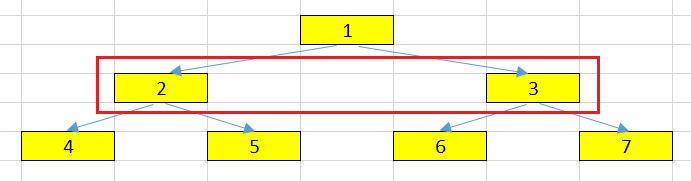
Width
The number of nodes in a level.
For example:
-
at the level = 2, we have two nodes such as 2 and 3.
-
at the level = 3, we have four nodes.
-
Wrapping up
-
With depth and level concept, remember that it compares with the root node.
-
With height concept, it compares with the leaf node.
Refer: