Table of contents
- Introduction to Struts 1 framework
- How Struts 1 works
- Core componenets in Struts 1 framework
- Wrapping up
Introduction to Struts 1 framework
Struts is an application development framework that is designed for and used with the popular J2EE platform. It cuts time out of the development process and makes developers more productive by providing them a series of tools and components to build applications. Struts is maintained as a part of Apache Jakarta project and is open source.
Struts 1 was first release of MVC based framework by the Apache Software foundation in May 2000.
How Struts 1 works
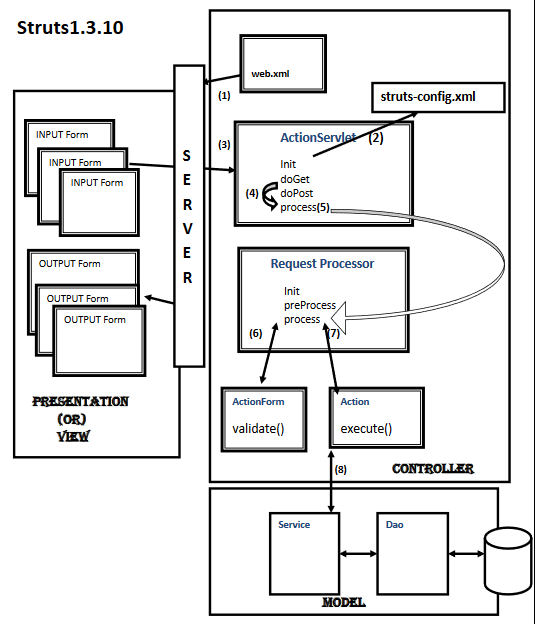
To describe the way Struts 1 work, we will seee the below image:
-
At deployment time or at the first user request, container will create ActionServlet instance, and it will call
initmethod. (Inweb.xmlfile, we have to configure it with*.doURL pattern). -
initmethod readstruts-config.xmland it will store that information intoModuleConfig configreference and when user sends a request,protected void initModuleFormBeans(ModuleConfig config)will create form bean instance and it will keep it in scope (request or session). -
When user sends a request, container will send that request to
void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)andvoid doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)methods. After that,doGet()anddoPost()methods will delegate tovoid process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)method of ActionServlet. -
process()method of ActionServlet will create one Singleton instance of aRequestProcessorand callvoid init(ActionServlet servlet, ModuleConfig moduleConfig)method ofRequestProcessor. Note that for each and every module ActionServlet will create one RequestProcessor object. -
Then,
process()method of ActionServlet will delegate request toprocess()method of RequestProcessor.process()method of RequestProcessor will callboolean processPreprocess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)method of the same class. IfprocessPreprocess()method returns true, then onlyprocess()method will do remain process. Otherwise, it will not process the request to next level. By default,processPreprocess()method’s implementation will return true. -
process()method ofRequestProcessorwill populate read user input form data and populates that form data into ActionForm instance by calling setter methods. -
Then, it will call the
ActionErrors validate(ActionMapping mapping, javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request)method for validation. It will return ActionErrors object which is the subclass of ActionMessage. -
In ActionMessage class,
isEmpty()method will check error messages what we added in our conditions:if (name.equals("")) { ae.add("name", new ActionMessage("mgs")); } -
If count is zero, then
process()method will redirect input page to the User for populating error messages. -
If error count is not equals to zero, the
process()method will create ActionClass object. In single factor (for first user request), it will call execute method of our Controller class. -
For that
execute()method, it pass (ActionMapping, ActionForm, HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) as execute method parameters. -
By using request or ActionForm parameter, we can read form data to process next Model layer classes.
-
From
execute()method,process()method of RequestProcessor will expect one ActionForward that is return type. In that ActionForward, we can configure the required page redirection configuration. -
Based on that configuration,
process()method will forward required configured page what we have configured under<forward>tag instruts-config.xmlfile.
Core componenets in Struts 1 framework
Belows are some main components that we need to understand:
-
ActionServlet is a front controller Servlet in Struts, and the only Servlet exists in Struts framework. Every request comming to Struts must first come to ActionServlet clss instance. When ActionServlet class call
init()method, ActionServlet readsstruts-config.xmlfile to get data and stores it into one ModuleConfig object.ModuleConfig object contains all 8
struts-config.xmlfile elements. Once aftermoduleConfigobject is created that object is passed into one new instance of RequestProcessor constructor.RequestProcessor reqProcessor = new RequestProcessor(this, moduleConfig);this is current ActionServlet class instance, and moduleConfig is ModuleConfig object.
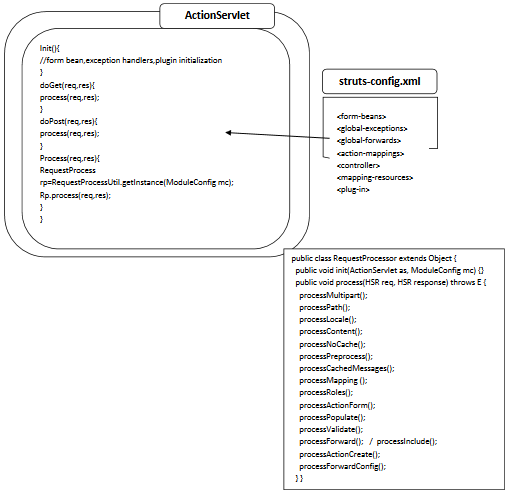
In the process() method, ActionServlet invokes process() method of RequestProcessor.
-
ModuleConfig
ModuleConfig contains the content of
struts-config.xmlfile. It contains allActionForm,Action,ActionForward,ActionMappingclass names.Whenever client request comes,
ActionServletsends request toRequestProcessor,RequestProcessorusesModuleConfigobject to find out theActionFormandActionclass names of the requested action path uri.
Wrapping up
- Understanding about the flows between components in Struts 1 helps us in coding, debugging.
Refer:
https://studylib.net/doc/9379291/struts-config.xml-file
http://tool.oschina.net/uploads/apidocs/struts-1.3.10/org/apache/struts/action/ActionServlet.html