In this article, we will dive into the MVC architectural pattern, to see how it works, … Because so many frameworks that use it, understanding mvc pattern will help you work with them confidently.
Let’s get started.
Table of contents
- Given Problem
- Analysis Problem
- Definition of MVC Pattern
- When to use
- Code C++/Javascript
- Application & Examples
Given Problem
Back in the 70’s, GUI applications or desktop applications is popular. Normally, they have two main responsibilities:
- Screen layout: defining the arrangement of the controls on the screen, together with their hierarchies structure with one other.
- Logic: behavior that cannot be easily programmed into the controls themselves.
So, the View and Logic will be always tightly coupling. We always have to take care everything when we change controls in the View. View and Logic do not develop parallel.
Analysis Problem
The root problem is that the View and Logic are always tightly coupling. So, we have to separate between the View and Logic part.
It is called Separated Presentation. The idea behind Separated Presentation is to make a clear division between domain objects that model our perception of the real world, and presentation objects that are the GUI elements we see on the screen.
So, the presentation part is made of the two remaining elements: View and Controller.
Finally, the logic part or the relavant to domain element is referred to as the Model.
–> MVC was born.

Definition of MVC Pattern
According to MVC pattern in wikipedia.com, we have the definition of it:
Model-View-Controller (usually known as MVC) is an architectural pattern commonly used for user interfaces that divides an application into three interconnected parts. This is done to separate internal representations of information from the ways information is presented to and accepted from the user. The MVC design pattern decouples these major components allowing for code reuse and parallel development.
Model
- The central of the pattern. It is the application’s dynamic data structure, independent of the user interface. It directly manages the data, logic and rules of the application.
- The Model doesn’t know anything about Views and Controllers.
View
- The presentation of application that users can interact with it.
- In some variations of MVC, the View does not directly interact with the Model.
- But originally, MVC use
Observer patternto know all changes from the Model to update the View part.
Controller
- The Controller’s job is to take the user’s input and figure out what to do with it.
- It means that this part is used to receive events from views, and will implement all actions to give data to the Model.
- And the Controller also will take all modifications from the Model, then creates some updates to the View.
This pattern was originally designed by Trygve Reenskaug during his time working on Smalltalk-80 (1979) where it was initially called Model - View - Controller. MVC went on to be described in depth in 1995’s Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software, which played a role in popularizing its use.
Below is the image about MVC pattern:
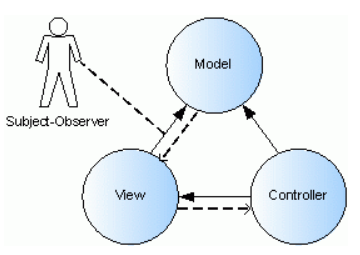
The dashed lines represent weakly typed aggregation and the solid lines strongly typed aggregation.
The Model maintains a pointer to the View, which allow it to send the View weakly typed change notifications. Since it is a weakly type relationship, the Model references the View only through a base class that allows it to send notifications to the View.
In contrast, the View knows exactly what kind of model it observers. It has a strongly typed pointer to the model that allows it to call any of the Model’s functions. The View also has a weakly typed relationship with the controller. The View is not tied to a specific type of controller, which means that different types of controllers can be used with the same View.
The Controller has pointers to both the Model and the View, knows the type of both. Because the Controller defines the behavior, it needs to know the type of both the Model and the View to translate user input into application response.
All above contents talk about traditional MVC pattern. Now, we will see the present MVC pattern can have any changes when compare to the traditional MVC pattern.
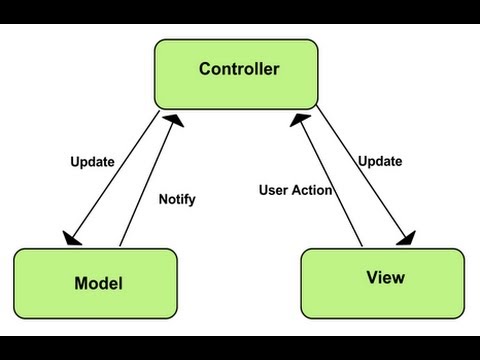
We can see that View and Model do not relate together. All actions between them must go through Controller.
When to use
- An application needs asynchronous communication on the back-end.
- An application has a functionality which results do not need to reload a full page, for example, commenting on a post while using Facebook or scrolling infinitely.
- Manipulation of data is mostly on the client side rather than server side.
- Same type of data is being delivered in different ways on a single page.
- When an application has many insignificant connections that are used to modify data (button, switches).
Benefits & Drawback
-
Benefits
-
Faster development process
Multiple developers can work simultaneously on the model, controller and views. The application developed by using MVC can be three times faster than application developed using other development patterns.
-
MVC enables logical grouping of related actions on a controller together. The views for a specific model are also group together.
-
Ability to provide multiple views
Models can have multiple views. Code duplication is very limited in MVC because it separates data and business logic from the display.
-
Support for asynchronous technique
MVC also supports asynchronous technique, which helps developers to develop an application that loads very fast.
-
MVC model returns the data without formatting
MVC pattern returns data without applying any formatting. So the same components can be used and called for use with any interface.
-
In some frameworks that use MVC pattern such as Spring, …, it will use Front Controller pattern.
Front Controller pattern will handle multiple incoming requests using single interface (controller).
Front Controller provides centralized control. We need to configure only one controller in web server instead of many.
Front Controller provides support rich communications to design our web application.
-
-
Drawbacks
- Increased complexity.
- Inefficiency of data access in View.
- Reduce the security because the Model can be embbeded in View.
-
In MVC pattern, View and Model can be interacted each other based on Observer pattern.
So, it means that we usually take some data logic into View. So, testing is really difficult when we do not know deeply the data logic.
Code Python
Source code about MVC pattern, we can referrence from this link https://github.com/DucManhPhan/Design-Pattern/tree/master/Architectural-pattern
Application & Examples
-
Nowadays, MVC pattern mostly is used in web application.
-
The Model is the module which interacts with the database (in the simplest designs, this could be directly the library which is used to query the database using SQL.)
-
The View is the module which generates HTML from the data.
-
The Controller contains all the other functionality of the server (E.g: it decides which page to display, generates dynamic contents, handles session and cookie data, …)
-
Wrapping up
-
The GoF do not refer to MVC as a design pattern, but rather consider it a set of classes to build a user interface. In their view, it’s actually a variation of three classical design pattern: the
Observer pattern,Strategy pattern, andComposite pattern. Depending on how MVC has been implemented in a framework, it may also use theFactoryandTemplate patterns. -
Views and controllers have a slightly different relationship. Controllers facilitate Views to respond to different user input and are an example of the Strategy pattern.
-
Both the relationship between View and Controller, View and Model is many-to-one.
-
Views are registered to get update or receive notification from Model based on
Observer pattern.
Refer:
The author of MVC pattern explains it
http://heim.ifi.uio.no/~trygver/themes/mvc/mvc-index.html
Create multiple controller in MVC pattern
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20453684/how-to-manage-multiple-forms-in-mvc-pattern
MVC Principles and Practice
https://docs.roguewave.com/stingray/11.1/html/sflug/8-9.html
https://crimsonpublishers.com/prsp/fulltext/PRSP.000505.php
https://blog.codinghorror.com/understanding-model-view-controller/
https://martinfowler.com/eaaDev/uiArchs.html
https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/learning-javascript-design/9781449334840/ch10s04.html
https://www.tomdalling.com/blog/software-design/model-view-controller-explained/
https://martinfowler.com/eaaDev/SeparatedPresentation.html
https://docs.roguewave.com/stingray/11.1/html/sflug/8-2.html
https://www.brainvire.com/six-benefits-of-using-mvc-model-for-effective-web-application-development/
https://medium.com/@matthewan/traditional-mvc-and-mvc-in-ios-development-2280d353b459
When MVC pattern not use
https://www.raywenderlich.com/7026-getting-started-with-mvp-model-view-presenter-on-android