Boost contains over 80 libraries for C++ programming language that supports for task and structures such as Linear Algebra, Image Processing, Pseudo random number generation, multithreading, regular expression and unit testing.
They range from general-purpose libraries like the smart pointer library, to operating system abstractions like Boost FileSystem, to libraries primarily aimed at other library developers and advanced C++ users, like the template metaprogramming (MPL) and domain-specific language (DSL) creation (Proto).
Before programming with C++ Boost Library, we have to intend to install the Boost library. The following is the steps to install:
- Download C++ Boost library in the Internet.
- Decompress this zip file.
- In the directory such as boost_1_68_0, run the “bootstrap.bat”.
- Finally, run the executable file: “b2”.
This image is our result when installing successfully.
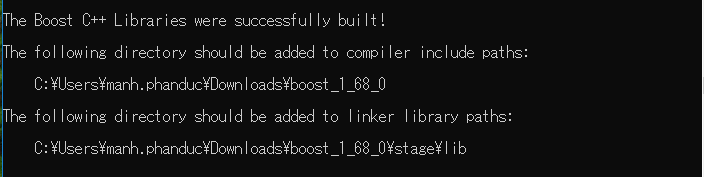
We can use the above paths to insert into our project.
Here, there are two ways to configure for your project in Visual Studio.
-
First way
In your properties’s project,
- Find the key “Additional Include Directories” in “C/C++\General”, add your path “…/boost_1_68_0”
- At “Linker\General”, find the key “Additional Library Directories”, add path “…/boost_1_68_0/stage/lib”.
-
Second way
Because there are some garbage files in your boost_1_68_0, then,you can delete them. Next, you will copy some neccessary folder into your folder by using the BCP tool.
Open the folder “C:\boost_1_68_0\tools\bcp”, call the cmd.exe. Then, run bjam.exe at this folder.
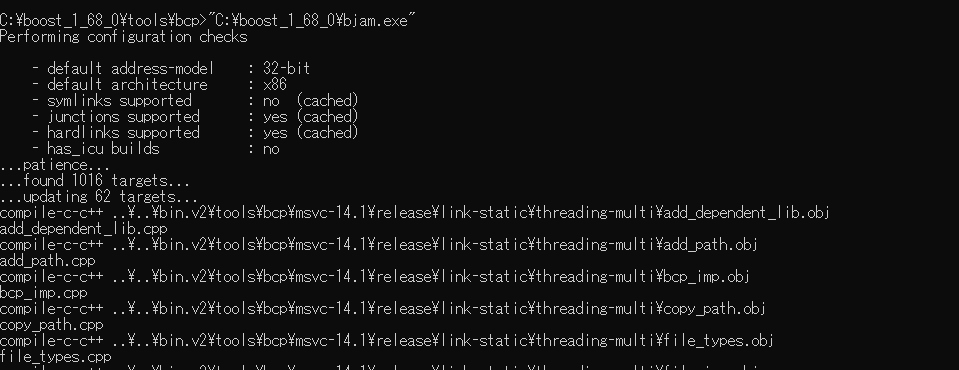
After running the bjam.exe, this creates the bcp.exe in the folder “C:\boost_1_68_0\bin.v2\tools\bcp\msvc-14.1\release\link-static\threading-multi”
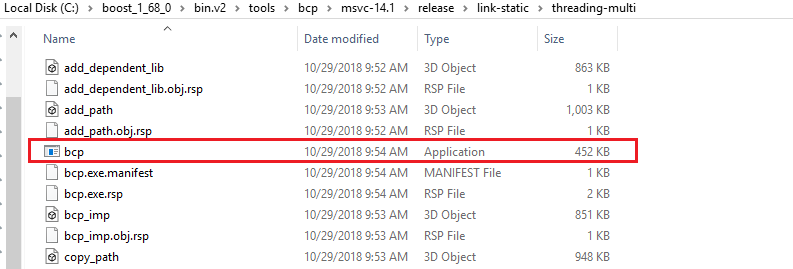
In order to get information about bcp, you can refer some the below links at the end of this article.
To get the subset of Boost libraries, at the folder “C:\boost_1_68_0\bin.v2\tools\bcp\msvc-14.1\release\link-static\threading-multi”, you can implement:
Ex:
bcp scoped_ptr –boost=”C:\boost_1_68_0” D:\project\boost_1_68_0\include\boost
bcp.exe regex –boost=”C:\boost_1_68_0” D:\project\boost_1_68_0\include\boost
- Make folder new with the same name at the different path - “D:\project\boost_1_68_0”.
- In the new foler “D:\project\boost_1_68_0”, create the nested foler “include\boost”, then, implement the command with bcp.exe. It is as same as the above command example.
- In the new foler “D:\project\boost_1_68_0”, create the nested foler “lib”, then, copy the library (that is relevant to your library which you want) of the old path “boost_1_68_0\stage\lib” to the folder that has just created, it is “boost_1_68_0\lib”.
- In your project properties, find the key “Additional Include Directories” in “C/C++\General”, add your path “./boost_1_68_0/include”.
- In your project properties, at “Linker\General”, find the key “Additional Library Directories”, add path “./boost_1_68_0/lib”.
Thanks for your reading.
Refer:
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_68_0/tools/bcp/doc/html/index.html
https://steveire.wordpress.com/2016/08/21/boost-dependencies-and-bcp/
How Boost automatically includes libraries
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_68_0/tools/bcp/doc/html/index.html
https://www.technical-recipes.com/2014/using-subset-boost-in-windows/
http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/bionic/man1/bcp.1.html
https://steveire.wordpress.com/2016/08/21/boost-dependencies-and-bcp/